Ivydene Gardens Home: |
READING THE TEXT IN RED ON THIS PAGE WILL MAKE IT EASIER FOR YOU TO USE EACH PAGE in my educational website.
THE 2 EUREKA EFFECT PAGES FOR UNDERSTANDING SOIL AND HOW PLANTS INTERACT WITH IT OUT OF 10,000:-
Explanation of Structure of this Website with User Guidelines Page for those photo galleries with Photos (of either ones I have taken myself or others which have been loaned only for use on this website from external sources)
Problems with electrical re-wire in my home, with the knowledge after the event that the client can do nothing about it, since NAPIT requires you to re-use the same contractor to fix the problems. Would you after reading these pages? We wrote the concerns about the electrical work on 21.03.21; Questions concerning electrics on 21.03.21 and re-wire narrative on 19.04.2021 which had no effect on the credit card company or NAPIT. So we commisioned the following report to see if that will make any difference.
Because we had paid part of the cost to Manderson Electrical Services Ltd using a credit card, then after we had contacted them and sent the report, the credit card company re-imbursed us. We then used that money towards a total removal of all wiring and total rewiring by the electrician who had produced the report. The above was a pointless waste of time - we have now had the house completely rewired again without any recompense from the original contractor's lies, thiefery and extremely dangerous work with the government body Napit being no help at all. The unfortunate consequence of either buying a house or having anything done to it is that you the owner can and will be totally screwed by the majority of the British Workforce. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Many of the trees in the pavements along the roads from Funchal Cathedral to the Forum are pollarded before being planted and pollarded later in their lives and then left to their own devices in most cases with no irrigation or feeding, so that the soil round their roots degenerates to its component rock. Maintenance seems to mostly take the form of tidying up the broken branches, perhaps bracing branches together to prevent their collapse, or cutting the trees down to the ground. I will be suggesting a possible change to make these trees healthier and prevent the town from turning into a volcano of heat. |
Pollarding, a pruning system involving the removal of the upper branches of a tree, promotes a dense head of foliage and branches. Traditionally, people pollarded trees for one of two reasons: for fodder to feed livestock or for wood. Wood pollards were pruned at longer intervals of eight to fifteen years, a pruning cycle tending to produce upright poles favored for fence rails and posts and boat construction. Nowadays, the practice is sometimes used for ornamental trees, such as crepe myrtles in southern states of the USA, although the resulting tree has a stunted form rather than a natural-looking crown. Pollarding tends to make trees live longer by maintaining them in a partially juvenile state and by reducing the weight and windage of the top part of the tree. Pollarding began with walled cities in Europe which did not have room for large trees. Although people who migrated to the United States from Europe continued the practice, experts have come to believe that pollarding older trees harms the tree. The smaller limbs grow from wood that is not as strong, and the weaker trees will not live as long and can be more easily damaged by storms. As with coppicing, only species with vigorous epicormic growth may be made into pollards. In these species (which include many broadleaved trees but few conifers), removal of the main apical stems releases the growth of many dormant buds under the bark on the lower part of the tree. Trees without this growth will die without their leaves and branches. Some smaller tree species do not readily form pollards, because cutting the main stem stimulates growth from the base, effectively forming a coppice stool instead. Examples of trees that do well as pollards include broadleaves such as beeches (Fagus), oaks (Quercus), maples (Acer), black locust or false acacia (Robinia pseudoacacia), hornbeams (Carpinus), lindens and limes (Tilia), planes (Platanus), horse chestnuts (Aesculus), mulberries (Morus), Eastern redbud (Cercis canadensis), tree of heaven (Ailanthus altissima), willows (Salix), and a few conifers, such as yews (Taxus). |
Pollarding, a pruning system in which the upper branches of a tree are removed, which encourages watersprouts. Water sprouts are shoots that arise from the trunk of a tree or from branches that are several years old, from latent buds. The latent buds might be visible on the bark of the tree, or submerged under the bark as epicormic buds. They are sometimes called suckers, although that term is more correctly applied to shoots that arise from below ground, from the roots, and a distance from the trunk. Vigorous upright water sprouts often develop in response to damage or pruning. The structure of water-sprout regrowth is not as strong as natural tree growth, and the shoots are more subject to diseases and pests. Adventitious shoots are also produced at the circumference of the cut trunk/branch. Coppicing is the practice of cutting tree stems to the ground to promote rapid growth of adventitious shoots. Adventitious buds are often formed after the stem is wounded or pruned. The adventitious buds help to replace lost branches. Adventitious buds and shoots also may develop on mature tree trunks when a shaded trunk is exposed to bright sunlight because surrounding trees are cut down, or in the case of the tree pollarded in the front garden of the Pestana Mirimar Garden from its own shade. The disadvantage for these shoots from the cut ends is that the growth comes from the water/nutrient bearing cells and is not supported by the heartwood beyond the cut, so is inherently weaker as well as not being the only new branch round that cut end. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
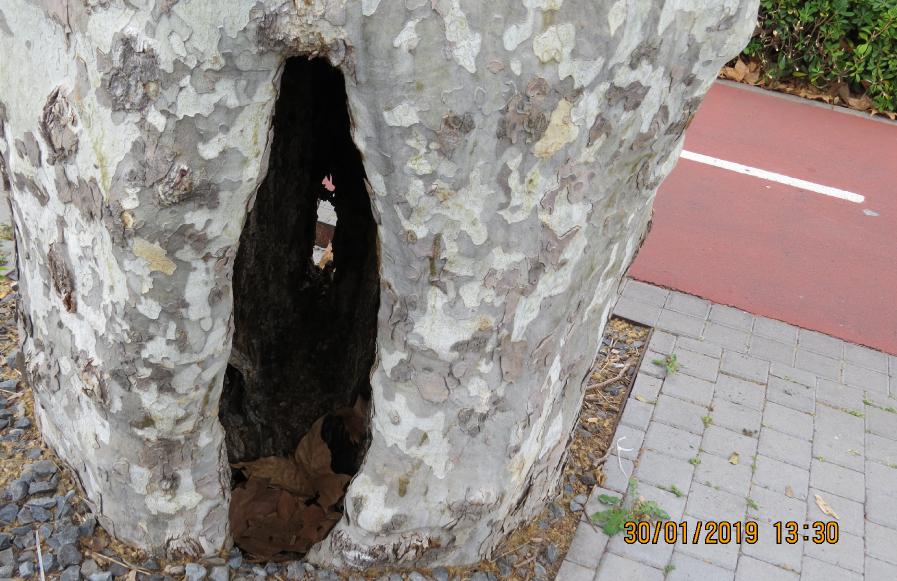
tree 21 forum end of 2 road junction with hole through trunk opposite enotel IIMG_6206.JPG This tree opposite Enotel Hotel has a hole through the trunk at and below ground level. Below is photos showing another hole in the trunk - it is likely that that hole has also rotted the heartwood of this trunk sufficiently to reach this hole below. I showed these photos to the reception staff in the Enotel Hotel and equired whether they minded that this tree might fall towards them and if they were concerned? I gave them my website name of www.ivydenegardens.co.uk and requested that instead of chopping that tree down, that it was high pressure-hosed inside the trunk to remove the loose rotten wood. Whilst still wet then apply expanded foam to fill the hole (empty bottles or cullet could also be used to reduce the cost. Apply coating of expanded foam, pour in the cullet or lay the empty bottles in rows. Apply more expanding foam, making sure that no cullet or empty bottle touches the heartwood).The expanded foam is poisonous and will kill any small organism eating it. Once the foam is set after 2 or 3 hours, then trim it and paint it with 2 coats of black masonry water-based plastic masonry paint - see below. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tree 21 forum end of 2 road junction with hole through trunk IMG_6203.JPG. This shows some more of the rotten tree heartwood from the opposite side to the above If you decide to cut the tree down, then why not replace it with one of your own native trees as specified in Madeira Plants and Flowers. Text and Photography Anonio da Costa. Published in Funchal, 2002. ISBN 972-9177-35-X. Please do not replant with Phoenix canariensis (Canary Palm) as shown on page 332. This book shows photos and details of 454 plants and flowers that can be seen in Madeira, either in cultivation or growing wild. One will find here 88 plants endemic from the Island, as well as 53 others which also occur in the Azores, the Canary Islands and /or Cape Verde - archipelagos which, together with that of Madeira, form the Macaronesia. The remaining species illustrated come from most other parts of the world.
tree 21 forum end of 2 road junction with hole through trunk opposite enotel IMG_0207 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tree 21 forum end of 2 road junction with hole through trunk opposite enotel IIMG_6208.JPG The hump on the trunk on the left is where a large branch was removed and the hole on the right is the same hole as in the photo above. You can see the Enotel Hotel sign in the background of this photo |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tree 21 forum end of 2 road junction with hole through trunk opposite enotel IMG_6204.JPG The position of this hole is indicated in the photo above. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
tree 21 forum end of 2 road junction with hole through trunk opposite enotel IIMG_6205.JPG Holding the camera above my head, I took this photo showing the damage inside this trunk. The position of this hole is shown in the "tree 21 forum end of 2 road junction with hole through trunk opposite enotel IIMG_6208.JPG" photo 2 rows above. There w ill be more pages showing further examples of damage to the trunks/branches of these trees in the pavements.
tree 21 forum end of 2 road junction with hole through trunk opposite enotel IMG_0206 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following is copy of the Site Map Page of Ivydene Gardens Evergreen Trees Gallery:- "Saving the Common Yew at St. Margarets Church, Rainham, Kent (written 31 July 2009 for the congregation). Over the years, damage has occurred to the branches coming from this multi-trunked yew tree. Some of this is where a branch has broken off or broken at the junction with its trunk leaving a jagged edge. When it rains, the water collects in this jagged edge and provides a carrier for rot bacteria to enter and break down the strength of the Heartwood. This has happened down the middle of most of the trunks. Mr Noakes (Churchwarden) and I are excavating and removing as much of this rot as possible before replacing it with Polycell Expanding Foam (which contains Diphenylmethane-4, 4-diisocyanate) and empty bottles. The empty bottles reduce the number of cans of Polycell Expanding Foam used. This Foam is normally used in the construction industry to fill the space between Windows and Walls and thus prevent draughts round the edge of the windows. In this case, it fills all the space occupied by the removed rot and if any beastie tries eating it, it will be killed by the cyanate in it. This also prevents the bacteria from having access to air/rain; thus hopefully stopping any further internal rot. Unfortunately the Foam is attacked by light, becomes brittle and flakes off, so we are painting it twice with Black Masonry Paint to prevent that. The Masonry Paint is a plastic film which is flexible, so if the tree moves the paint will move with it rather than cracking apart . |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following Diagram is from Wikipedia.org/wiki/wood.jpg:-
When a tree grows it has Bark on the outside, which is the tree's growth area.
Inside that are the xylem sections which are responsible for the transport of water and soluble mineral nutrients from the roots throughout the plant.
Inside that is Heartwood. Heartwood is wood that has become more resistant to decay as a result of deposition of chemical substances (a genetically programmed process). Once heartwood formation is complete, the heartwood is dead. Some uncertainty still exists as to whether heartwood is truly dead, as it can still chemically react to decay organisms, but only once (Shigo 1986, 54).
The Bark and Xylem sections on the outer part of the trunk or branch are quite thin. The Heartwood does the structural support of the entire tree. The Heartwood is dead and therefore if anything attacks it, the tree cannot defend itself from woodworm, wet rot, dry rot, honey fungus etc. Therefore if the Heartwood is exposed it needs to be defended against attack. It used to be done using concrete, but unfortunately concrete shrinks when it cures and therefore it allows for air and water to get at the heartwood again. If the tree bark and cambium layer is broken apart all the way round a trunk so that the lower liquid in it cannot connect with the liquid in the higher trunk, then all the trunk above that will die. Some of the branches have fallen away from the trunk and are almost on the ground, but are supported on thin branches from them to the ground (the next paragraph explains how we will provide nutrients for these thin branches in the ground). We will replace the rot at the trunk-branch connection with Foam and apply the Masonry Paint. All the exposed Heartwood on these branches and the rest of the tree will also be liberally painted with the Black Masonry Paint to prevent woodworm or anything else from eating or changing it thus removing its function of holding up the rest of the tree. The colour of the paint is immaterial but black is easy to buy and does not draw attention to the fact that 20% of the tree will have to be painted, unless you wish us to create a painted work of art! The roots of a tree are generally embedded in earth, providing anchorage for the above-ground biomass and absorbing water, air and nutrients from the soil. It should be noted, however, that while ground nutrients are essential to a tree's growth the majority of its biomass comes from carbon dioxide absorbed from the atmosphere. Some of the area round the tree has been used to dump the subsoil from digging graves. Subsoil has no nutrients and so is not a benefit for the yew tree. We can change the subsoil into topsoil by mulching it with organic material which the worms will take down into this subsoil. It is suggested that all the flowers and foliage from the church and churchyard are placed on top of the pile of branches on the ground next to the trunk between 9.00 and 10.00 o’clock when looking at the tree from Station Road. These can then be spread over the area (under the tree not cut by the lawnmowers) before covering it over with a thin layer of shreddings of tree prunings to make it look tidy. The shreddings will come from professional tree surgeons; and as they decompose this mulch will replenish the minerals for the tree. You will notice in a natural wood, that when the leaves and branches fall on the ground, they are not removed but are recycled by the worms and bacteria for the trees to reuse the minerals for future growth. This new mulch will duplicate this natural process in a neater fashion. This repair and restorative work will take some time for David and I to complete |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Yew Tree of St Margaret’s Church, Rainham, Kent, written by Clifford Hansford. Contributory Member of the Ancient Yew Group www.ancient-yew.org
Observations of the tree’s current restoration/conservation work now nearing completion, 15th February 2010. The following observations have been recorded in response to a request from Tim Hills (Ancient Yew Group) for information relating to the particular method currently being used to rescue and protect the above yew from further decay. It is hoped that the information will be of use to assist Mr Russell Ball, President of the United Kingdom & Ireland International Society of Arboriculture, in assessing the methods’ acceptability for such a task. Having learned of the tree’s plight from a colleague at the Kent Wildlife Trust, and visited the yew on Sat’ 13th February with Mr Chris Garnons-Williams, who is undertaking the work, my understanding of the situation is as follows:-
Notes: An assortment of different size bottles, ranging from whiskey and wine (large bottles) to the smaller fruit juice bottles, are used depending on the size of the cavities/gaps to be filled. In hindsight, Chris would recommend the use of high-pressure water to remove the decayed wood rather than screwdrivers and other blade-type implements. The residual water left from the process would help to set the expandable polystyrene foam. Work started in August 2009, with a break during the cold weather, and is still ongoing. A further five to ten days is anticipated for completion. All old, firm wood has been left in situ. Lots of new shoots are now forming. Between Chris and myself we were able to measure the girth of the yew as being 26 feet at its base. It just so happened that on the day Chris and I met for the first time (13 Feb 2010), the church had its annual open day. This gave me an opportunity to learn from church members how very determined they are to preserve this much respected yew.
Western facing aspect.
View of Eastern aspect.
View of Southern aspect
View of Northern aspect which indicates the open centre before preservation action.
View of Northern aspect with Clifford Hansford - after preservation action.
Bottle-filled foam repair.
View showing filled split in a limb growing from a fallen branch.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
IMPROVING ST BARTHOLOMEWS CHURCHYARD, CAN YOU HELP? I visited this churchyard on 19 May 2013 and found that the clearing work I had started in July 1999 had been considerably further extended, so now there is a glorious view beyond the church of the surrounding hills and valley. The current very elderly yew trees on the left as one comes into the churchyard have rotten open trunks, which could have the earth removed from inside together with the heartwood rot using trowels and chisels. Then, use a high-pressure water hose to remove yet more of the internal rot, before following what was done to protect the Common Yew at St. Margarets Church, Rainham, Kent as detailed in this Introduction Page. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For educational purposes, so that people following best practice can fully understand why the evergreen trees never lose their leaves; here are the written facts from The Book of Nature Myths by Florence Holbrooke:-
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This website is being created by Chris Garnons-Williams of Ivydene Horticultural Services from it's start in 2005. I am requesting free colour photographs of any plants grown in or sold in the United Kingdom to add to the plants in the Plant Photographic Galleries and Butterfly photographs for the Butterfly on Plant Photographic Galleries. |
Site design and content copyright ©April 2007. Page structure amended October 2012. Page structure changed February 2019 for pages concerning Trees in pavements alongside roads in Madeira. Chris Garnons-Williams. DISCLAIMER: Links to external sites are provided as a courtesy to visitors. Ivydene Horticultural Services are not responsible for the content and/or quality of external web sites linked from this site. |
It should be remembered that nothing is sold from this educational site, it simply tries to give you the best advice on what to use and where to get it (About Chris Garnons-Williams page details that no payment or commision to or from any donor of photos or adverts I place on the site in the Useful Data or other sections is made to Chris Garnons-Williams or Ivydene Horticultural Services). This website is a hobby and not for direct commercial gain for Ivydene Horticultural Services. There is no Google Adscenes or Search Facility in this website. The information on this site is usually Verdana 14pt text (from December 2023, this is being changed from 14pt to 10pt) and all is in tabular form. This can be downloaded and sorted using WORD or other word-processing software into the order that you personally require, especially for soil subsidence, the Companion Planting Tables and the pages in the Plants section. This would be suitable for use in education as well. I put jokes in at various places to give you a smile. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There’s A Genius Street Artist Running Loose In The Streets. Let’s Hope Nobody Catches Him!
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Worms in Love. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following is from "Some time around 600 million years ago, green algae began to move out of shallow fresh waters and onto the land. They were the ancestors of all land plants... Today, plants make up to 80% of the mass of all life on Earth and are the base of the food chains that support nearly all terrestrial organisms.... But the algal ancestors of land plants had no roots, no way to store or transport water, and no experience in extracting nutrients from solid ground. How did they manage the fraught passage onto dry land? ... It was only by striking up new relationships with fungi that algae were able to make it onto land. These early alliances evolved into what we now call mycorrhizal relationships. Today, more than 90% of all plant species depend on mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhizal associations are the rule not the exception: a more fundamental part of planthood than fruit, flowers, leaves, wood or even roots.... For the relationship to thrive, both plant and fungus must make a good metabolic match. In photosynthesis, plants harvest carbon from the atmosphere and forge the energy-rich carbon compounds - sugars and lipids - on which much of the rest of life depends. By growing within plant roots, mycorrhizal fungi acquire privileged access to these sources of energy: they get fed. However, photosynthesis is not enough to support life. Plants and fungi need more than a source of energy. Water and minerals must be scavenged from the ground - full of textures and micropores, electrically charged cavities and labyrinthine rot-scapes. Fungi are deft rangers in this wilderness and can forage in a way that plants can not. By hosting fungi within their roots, plants gain hugely improved access to these sources of nutrients. They, too, get fed. By partnering, plants gain a prosthetic fungus, and fungi gain a prosthetic plant. Both use the other to extend their reach.... By the time the first roots evolved, the mycorrhizal association was already some 50 million years old. Mycorrhizal fungi are the roots of all subsequent life on land. Today, hundreds of millions of years later, plants have evolved, faster-growing, opportunistic roots that behave more like fungi. But even these roots cannot out-manoeuvre fungi when it comes to exploring the soil. Mycorrhizal hyphae are 50 times finer than the finest roots and can exceeed the length of a plant's roots by as much as a 100 times. Their mycelium makes up between a third and a half of the living mass of soils. The numbers are astronomical. Globally, the total length of mycorrhizal hyphae in the top 10 centimetres (4 inches) of soil is around half the width of our galaxy (4.5 x 10 to the power 17 kilometres versus 9.5 x 10 to the power 17 kilometres). If these hyphae were ironed into a flat sheet, their combined surface area would cover every inch of dry land on Earth 2.5 times over.... In their relationship, plants and mycorrhizal fungi enact a polarity: plant shoots engage with the light and air, while the fungi and plant roots engage with the solid ground. Plants pack up light and carbon dioxide into sugars and lipids. Mycorrhizal fungi unpack nutrients bound up in rock and decomposing material. These are fungi with a dual niche: part of their life happens within the plant, part in the soil. They are stationed at the entry point of carbon into terrestrial life cycles and stitch the atmosphere into relation with the ground. To this day, mycorrhizal fungi help plants cope with drought, heat and many other stresses life on land has presented from the very beginning, as do the symbiotic fungi that crowd into plant leaves and stems. What we call 'plants' are in fact fungi that have evolved to farm algae, and algae that have evolved to farm fungi.... Mycorrhizal fungi can provide up to 80% of a plant's nitrogen, and as much as 100% of its phosphorus. Fungi supply other crucial nutrients to plants, such as zinc and copper. They also supply plants with water, and help them to survive drought as they have done since the earliest days of life on land. In return, plants allocate up to 30% of the carbon they harvest to their mycorrhizal partners.... And yet mycorrhizal fungi do more than feed plants. Some describe them as keystone organisms; others prefer the term 'ecosystem engineers'. Mycorrhizal mycelium is a sticky living seam that holds soil together; remove the fungi, and the ground washes away. Mycorrhizal fungi increase the volume of water that the soil can absorb, reducing the quantity of nutrients leached out of the soil by rainfall by as much as 50%. Of the carbon that is found in soils - which, remarkably, amounts to twice the amount of carbon found in plants and the atmosphere combined - a substantial proportion is bound up in tough organic compounds produced by mycorrhizal fungi. The carbon that floods into the soil through mycorrhizal channels supports intricate food webs. Besides the hundreds or thousands of metres of fungal mycelium in a teaspoon of healthy soil, there are more bacteria, protists, insects and arthropods than the number of humans who have ever lived on Earth. Mycorrhizal fungi can increase the quality of a harvest. They can also increase the ability of crops to compete with weeds and enhance their resistance to diseases by priming plant's immune systems. They can make crops less susceptible to drought and heat, and more resistant to salinity and heavy metals. They even boost the ability of plants to fight off attacks from insect pests by stimulating the production of defensive chemicals... But over the course of the twentieth century, our neglect has led us into trouble. In viewing soils as more or less lifeless places, industrial agricultural practices have ravaged the undergound communities that sustain the life we eat.... A large study published in 2018 suggested that the 'alarming deterioration' of the health of trees across Europe was caused by a disruption of their mycorrhizal relationships, brought about by nitrogen pollution." from Before Roots chapter by Merlin Sheldrake.
"We do know, that this fragile, generative world has been damaged by intensive farming, pollution, deforestation and global heating. A third of the planet's land has been severely degraded and 24 billion tons of fertile soil are destroyed every year through intensive farming, according to the Global Land Outlook. Topsoil is where 95% of the planet's food is grown and is very delicate. It takes more than 100 years to build 5mm of soil, and it can be destroyed shockingly easily. This destruction and degradation of the soil is created by intensive farming practices such as heavy mechanised soil tilling, which loosens and rips away any plant cover, leaving the soil bare. It is also caused by the overgrazing of animals, as well as forest fires and heavy construction work. These factors disturb the soil and leave it exposed to erosion from wind and water, damaging the complicated systems underneath its top layer... We are losing good soil at an estimated 100 times faster rate than we can remake and heal it. The world's soils are thought to store approximately 15 thousand million tonnes of carbon - 3 times as much as all of our planet's terrestrial vegetation combined. Soils hold twice as much carbon as the atmosphere, and when soil disintegrates, the carbon is released. In the last 40 years the soil in the UK's croplands lost 10% of the carbon it could store. In a time of climate crisis, soil's quiet potency, its ability to store carbon safely, is utterly essential to our future survival.... We know that soils are being destroyed, and that with that comes a higher risk of floods, and a more unpredictable and unreliable food and water system. An Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecostem Services report in 2018 told us clearly that land degradationis already putting the welfare of two-fifths of humanity at risk, and that urgent action is needed to avoid further danger. There are many things we can do to protect soils, and the organisms, plants and connections that thrive within them. Actions that can support and heal soil structure include
Such regimes allow soil structure to remain intact, and protect the soil by allowing crop residues to stay on the surface. " from Strange Soil chapter by Rebecca Tamas. |
Due to intensive farming techniques and chemical fertilisers this has occurred:- The BBC has produced an article as to why modern food as lost its nutrients. |
The following about trees in pavements show why when the roots are denied access to air, water and nutrients even the fungi cannot work to support the trees. Pavements of Funchal, Madeira |
The following addition of this mulch improved the clay soil, so that A 150mm deep mulch of mixed peat, sharp washed sand and horticultural grit was applied on top of a heavy clay soil to improve its structure, and stop the plants therein from drowning, at £10 a square metre. The mix was:
The following was then sent to me:-
and the following was sent to me in October 2004:- An unsuccessful planting scheme had left bare areas of garden as plants failed to survive winter in the waterlogged clay soil. The loss of numerous plants and the cost of replacing them had left us disheartened. It was evident that remedial action was need in the form of a mixture of gravel, sand and peat to create an organic loam. Approximately six inches was added in April and left to settle and do its job. By July there was a noticeable difference in the quality of the soil and the plants. Shrubs with sparse, mottled leaves were looking glossy and robust, overall growth had increased (including the weeds!) and the soil was holding its moisture well. But the biggest difference came in the confidence it gave us to transform the garden. The borders used to be a no-go area between May and September as the clay baked and cracked, but the new soil was easy to handle and weeds could be successfully removed. We realised that there are no quick fixes - the key to a healthy garden is rich, nutritous soil. Once our plants began to thrive we were optimistic that, with good advice, we could create a garden to be proud of. |
More Details |
Cultural Needs of Plants "Understanding Fern Needs |
|
It is worth remembering that especially with roses that the colour of the petals of the flower may change - The following photos are of Rosa 'Lincolnshire Poacher' which I took on the same day in R.V. Roger's Nursery Field:- |
|
Closed Bud |
|
Opening Bud |
|
Juvenile Flower |
|
Older Juvenile Flower |
|
Middle-aged Flower - Flower Colour in Season in its |
|
Mature Flower |
|
Juvenile Flower and Dying Flower |
|
Form of Rose Bush |
There are 720 roses in the Rose Galleries; many of which have the above series of pictures in their respective Rose Description Page. So one might avoid the disappointment that the 2 elephants had when their trunks were entwined instead of them each carrying their trunk using their own trunk, and your disappointment of buying a rose to discover that the colour you bought it for is only the case when it has its juvenile flowers; if you look at all the photos of the roses in the respective Rose Description Page!!!! |
|
There are 180 families in the Wildflowers of the UK and they have been split up into 22 Galleries to allow space for up to 100 plants per gallery. Each plant named in each of the Wildflower Family Pages may have a link to:- its Plant Description Page in its Common Name in one of those Wildflower Plant Galleries and it does have links:- to external sites to purchase the plant or seed in its Botanical Name, to see photos in its Flowering Months and to read habitat details in its Habitat Column. |
|
Links to external websites like the link to "the Man walking in front of car to warn pedestrians of a horseless vehicle approaching" would be correct when I inserted it after March 2007, but it is possible that those horseless vehicles may now exceed the walking pace of that man and thus that link will currently be br My advice is Google the name on the link and see if you can find the new link. If you sent me an email after clicking Ivydene Horticultural Services text under the Worm Logo on any page, then; as the first after March 2010 you would be the third emailer since 2007, I could then change that link in that 1 of the 15,743 pages. Currently (August 2016). Other websites provide you with cookies - I am sorry but I am too poor to afford them. If I save the pennies from my pension for the next visitor, I am almost certain in March 2023, that I could afford to make that 4th visitor to this website a Never Fail Cake. I would then be able to save for more years for the postage. |
UKButterflies Larval Foodplants website page lists the larval foodplants used by British butterflies. The name of each foodplant links to a Google search. An indication of whether the foodplant is a primary or secondary food source is also given. Please note that the Butterfly you see for only a short time has grown up on plants as an egg, caterpillar and chrysalis for up to 11 months, before becoming a butterfly. If the plants that they live on during that time are removed, or sprayed with herbicide, then you will not see the butterfly. |
||||
Plants used by the Butterflies follow the Plants used by the Egg, Caterpillar and Chrysalis as stated in |
||||
Plant Name |
Butterfly Name |
Egg/ Caterpillar/ Chrysalis/ Butterfly |
Plant Usage |
Plant Usage Months |
Egg, |
1 egg under leaf. |
10 days in May-June |
||
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches encircling the branch of the food plant. |
Hatches after 18-22 days in April. |
||
Egg, |
Groups of eggs on upper side of leaf. |
- |
||
Egg, |
1 egg at base of plant. |
Late August-April |
||
Egg, |
Groups of eggs on upper side of leaf. |
- |
||
Egg, |
1 egg laid on underside of leaflets or bracts. |
7 days in June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg laid on underside of leaflets or bracts. |
7 days in June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg laid under the leaf or on top of the flower. |
7 days in August. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of a flower bud on its stalk. |
7 days. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of a flower bud on its stalk. |
7 days. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg under leaf. |
10 days in May-June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
2 weeks |
||
Cabbages - Large White eats all cruciferous plants, such as cabbages, mustard, turnips, radishes, cresses, nasturtiums, wild mignonette and dyer's weed |
Egg,
|
40-100 eggs on both surfaces of leaf. |
May-June and August-Early September. 4.5-17 days. |
|
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of leaf. |
May-June and August. 7 days. |
||
Cabbages:- |
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of leaf. |
July or August; hatches in 3 days. |
|
Cabbages:- |
Egg, |
1 egg laid in the tight buds and flowers. |
May-June 7 days. |
|
Cherry with |
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches encircling the branch of the food plant. |
Hatches after 18-22 days in April. |
|
Egg, |
Groups of eggs on upper side of leaf. |
- |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
10 days in May-June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
6 days in May-June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg under leaf. |
|
||
|
(Common CowWheat, Field CowWheat) |
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 16 days in June. |
|
Currants |
Egg, |
Groups of eggs on upper side of leaf. |
|
|
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 20 days in July. |
||
Dog Violet with |
Egg, |
1 egg on oak or pine tree trunk |
15 days in July. |
|
Dog Violet with |
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf or stem. |
Hatches after 15 days in May-June. |
|
Dog Violet with |
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf or stem. |
Hatches after 10 days in May-June. |
|
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of a flower bud on its stalk. |
7 days. |
||
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches encircling the branch of the food plant. |
Hatches after 18-22 days in April. |
||
False Brome is a grass (Wood Brome, Wood False-brome and Slender False-brome) |
Egg, |
1 egg under leaf. |
... |
|
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 20 days in July. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg laid on underside of leaflets or bracts. |
7 days in June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf or stem. |
Hatches after 10 days in May-June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of a flower bud on its stalk. |
7 days. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg laid under the leaf or on top of the flower. |
7 days in August. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. 5 or 6 eggs may be deposited by separate females on one leaf. |
14 days in July-August. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of a flower bud on its stalk. |
7 days. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg laid in the tight buds and flowers. |
May-June 7 days. |
||
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 20 days in July. |
||
Egg, |
Groups of eggs on upper side of leaf. |
|
||
Egg, |
1 egg under leaf. |
1 then |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of a flower bud on its stalk. |
7 days. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg at base of plant. |
Late August-April. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
10 days in May-June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
2 weeks |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
6 days in May-June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of leaf. |
May-June and August. 7 days. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. 5 or 6 eggs may be deposited by separate females on one leaf. |
14 days in July-August. |
||
Narrow-leaved Plantain (Ribwort Plantain) |
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 16 days in June. |
|
Narrow-leaved Plantain (Ribwort Plantain) |
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 16 days in June. |
|
Nasturtium from Gardens |
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of leaf. |
May-June and August. 7 days. |
|
Egg, |
1 egg on tree trunk |
15 days in July. |
||
Mountain pansy, |
Egg, Chrysalis |
1 egg laid under the leaf or on top of the flower. |
7 days in August. 3 weeks in September |
|
Egg, |
1 egg on tree trunk. |
15 days in July. |
||
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 20 days in July. |
||
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches encircling the branch of the food plant. |
Hatches after 18-22 days in April. |
||
Egg, |
Groups of eggs on upper side of leaf. |
- |
||
Egg, |
1 egg under leaf. |
|
||
Egg, |
1 egg laid under the leaf or on top of the flower. |
7 days in August. |
||
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches encircling the branch of the food plant. |
Hatches after 18-22 days in April. |
||
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 16 days in June. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of a flower bud on its stalk. |
7 days. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of a flower bud on its stalk. |
7 days. |
||
Egg, |
Groups of eggs on upper side of leaf. |
|
||
Egg, |
1 egg under leaf. |
|
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
2 weeks |
||
Trefoils 1, 2, 3 |
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
6 days in May-June. |
|
Egg, |
Groups of eggs on upper side of leaf. |
- |
||
Egg, |
1 egg laid on underside of leaflets or bracts. |
7 days in June. |
||
Violets:- |
Egg, |
1 egg on underside of leaf or on stalk. |
July-August for 17 days. |
|
Violets:- |
Egg, |
1 egg on stem or stalk near plant base. |
July to hatch in 8 months in March. |
|
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. |
2 weeks. |
||
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches encircling the branch of the food plant. |
Hatches after 18-22 days in April. |
||
Egg, |
1 egg on leaf. 5 or 6 eggs may be deposited by separate females on one leaf. |
14 days in July-August. |
||
Willow |
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches encircling the branch of the food plant. |
Hatches after 18-22 days in April. |
|
Egg, |
Eggs laid in batches on the under side of the leaves. |
Hatches after 20 days in July. |
||
Plants used by the Butterflies |
||||
Plant Name |
Butterfly Name |
Egg/ Caterpillar/ Chrysalis/ Butterfly |
Plant Usage |
Plant Usage Months |
Asters |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
|
|
Runner and Broad Beans in fields and gardens |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
April-June or July-September. |
|
Aubretia in gardens |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
May-June or August till killed by frost and damp in September-November |
|
Butterfly |
Eats sap exuding from trunk. |
April-Mid June and Mid July-Early September for second generation. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
20 days. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
May-June |
||
Holly Blue |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
April-Mid June and Mid July-Early September for second generation. |
|
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
July-October. |
||
Buddleias |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
July-October. |
|
Wood White |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
May-June. |
|
Cabbage and cabbages in fields |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
April-June or July-September. |
|
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
July-October |
||
Adonis Blue |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
1 Month during Mid-May to Mid-June or during August-September |
|
Pale Clouded Yellow |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
May-June or August till killed by frost and damp in September-November |
|
Cow-wheat |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
June-July |
|
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
May-June |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
April-Mid June and Mid July-Early September for second generation. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
3 weeks between May and September |
||
Germander Speedwell (Veronica chamaedrys - Birdseye Speedwell) |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
June-July |
|
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
July-October. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
30 days in May-June. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
May-September |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
May-June for 18 days. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
July-October |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
1 Month. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
July-October. |
||
Painted Lady |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
July-October. |
|
Marigolds in gardens |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
May-June or August till killed by frost and damp in September-November |
|
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
1 Month during Mid-May to Mid-June or during August-September. |
||
Michaelmas Daisies |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
July-October |
|
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
April-June or July-September. |
||
Narrow-leaved Plantain (Ribwort Plantain) |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
June-July |
|
Nasturtiums in gardens |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
April-June or July-September |
|
Butterfly |
Eats sap exuding from trunk. |
April-Mid June and Mid July-Early September for second generation. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
June. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
May-June. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
July-October. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
July-May |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
7 weeks in July-August. |
||
Comma |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
July-October. |
|
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
3 weeks between May and September |
||
Trefoils 1, 2, 3 |
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
1 Month during Mid-May to Mid-June or during August-September |
|
Butterfly |
Eats nectar. |
20 days in August. |
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
June.
|
||
Butterfly |
Eats nectar |
June-July |
||
Apple/Pear/Cherry/Plum Fruit Tree Blossom in Spring |
Butterfly |
Eats Nectar |
April-May |
|
Rotten Fruit |
Butterfly |
Drinks juice |
July-September |
|
Tree sap and damaged ripe fruit, which are high in sugar |
Butterfly |
Hibernates inside hollow trees or outhouses until March. Eats sap or fruit juice until April. |
10 months in June-April |
|
Wild Flowers |
Large Skipper |
Butterfly |
Eats Nectar |
June-August |
Links to the other Butterflies:- Black Hairstreak |
Topic - Wildlife on Plant Photo Gallery. Some UK native butterflies eat material from UK Native Wildflowers and live on them as eggs, caterpillars (Large Skipper eats False Brome grass - Brachypodium sylvaticum - for 11 months from July to May as a Caterpillar before becoming a Chrysalis within 3 weeks in May) chrysalis or butterflies ALL YEAR ROUND. |
Wild Flower Family Page (the families within "The Pocket Guide to Wild Flowers" by David McClintock & R.S.R. Fitter, Published in 1956 They are not in Common Name alphabetical order and neither are the common names of the plants detailed within each family. The information in the above book is back-referenced to the respective page in "Flora of the British Isles" by A.R. Clapham of University of Sheffield, |
||
When you look at the life history graphs of each of the 68 butterflies of Britain, you will see that they use plants throughout all 12 months - the information of what plant is used by the egg, caterpillar, chrysalis or butterfly is also given in the above first column.
THE LIFE AND DEATH OF A FLAILED CORNISH HEDGE - This details that life and death from July 1972 to 2019, with the following result:- End note, June 2008. I hear spring vetch has been officially recorded somewhere in West Cornwall and confirmed as a presence in the county, so perhaps I can be permitted to have seen it pre-1972 in the survey mile. I wonder where they found it? It's gone from hedges where it used to be, along with other scarcities and so-called scarcities that used to flourish in so many hedges unrecorded, before the flail arrived. I have given careful thought to including mention of some of the plants and butterflies. So little seems to be known of the species resident in Cornish hedges pre-flail that I realise some references may invite scepticism. I am a sceptic myself, so sympathise with the reaction; but I have concluded that, with a view to re-establishing vulnerable species, it needs to be known that they can with the right management safely and perpetually thrive in ordinary Cornish hedges. In future this knowledge could solve the increasingly difficult question of sufficient and suitable sites for sustainable wild flower and butterfly conservation - as long as it is a future in which the hedge-flail does not figure.
CHECK-LIST OF TYPES OF CORNISH HEDGE FLORA by Sarah Carter of Cornish Hedges Library:-
Titles of papers available on www.cornishhedges.co.uk:-
THE GUILD OF CORNISH HEDGERS is the non-profit-making organisation founded in 2002 to support the concern among traditional hedgers about poor standards of workmanship in Cornish hedging today. The Guild has raised public awareness of Cornwall's unique heritage of hedges and promoted free access to the Cornish Hedges Library, the only existing source of full and reliable written knowledge on Cornish hedges." |
||||
SOIL PAGE MENU Soil Introduction - How does Water act in Soil SOIL SUBSIDENCE
Soil Site Map |
Click on Black or White box in Colour of Month. |
LATE SUMMER GALLERY PAGES FOLIAGE COLOUR BULB, CORM, RHIZOME AND TUBER INDEX - There are over 700 bulbs in the bulb galleries. The respective flower thumbnail, months of flowering, height and width, foliage thumbnail, |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Besides the above Bulb Flower Colour Comparison Pages, you also have the following Comparison Pages:- |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Late Summer INDEX link to Bulb Description Page |
Flower Colour with Flower Thumbnail |
Flowering Months Mat, |
Height x Width in inches (cms) - Seed Head Thumbnail Soil Sun Aspect Soil Moisture |
Foliage Colour |
Bulb Use |
Comments |
PLANTS PAGE PLANT USE Groundcover Height Poisonous Cultivated and UK Wildflower Plants with Photos
Following parts of Level 2a, |
PLANTS PAGE MENU
|
PLANTS PAGE MENU
Photos - 12 Flower Colours per Month in its Bloom Colour Wheel Gallery
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Acis "They are excellent for cutting and make a good display either in a bed or in a thin woodland. They also do quite well in grass, which must not be mown until their leaves begin to die down. "Indoor Culture in Window-boxes - Plant in clumps during October, 3 inches (7.5 cms) deep, 2 inches (5 cms) apart. These are excellent for a site in partial shade, but will only succeed if left undisturbed for 2 or 3 years. Suitable varieties are Leucojum aestivum 'Gravetye Giant' and Leucojum vernum." from Indoor Bulb Growing by Edward Pearson. Published by Latimer House Limited in 1953. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Acis autumnalis |
White
|
August, September, |
4-6 x 4 |
Dark Green grass-like foliage, often being produced shortly after the flower spike. |
Plant at edge of bed. Use in rock garden. Cut flower. Thin woodland or shade from shrubs. Naturalize in grass. |
In autumn it throws up leafless stems from which it bears 2-4 bell shaped white flowers, often with red bases to them. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Acis autumnalis pulchellum - |
White
|
August, September, |
8 x 4 |
Dark Green grass-like foliage being produced at the same time as the flower spike. |
Plant at edge of bed. Use in rock garden. Cut flower. Thin woodland or shade from shrubs. Naturalize in grass. |
Plant with 1 or 2 inches (2.5 or 5 cms) of soil over the tops of the bulbs towards the front of a bed in an area where they can be left undisturbed. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Acis |
Pure White flowers on 4-8 inch stems
|
September, 6 petal, bell-shaped flowers in spike. |
4 x 2 |
Dark Green grass-like foliage being produced at the same time as the flower spike. |
Plant at edge of bed. Use in rock garden. Cut flower. Thin woodland or shade from shrubs. Naturalize in grass. |
Plant with 1 or 2 inches (2.5 or 5 cms) of soil over the tops of the bulbs towards the front of a bed in an area where they can be left undisturbed. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Acis valentinum |
White
|
February, March, |
10 x 12 |
Thin Grey-Green leaves being produced after the flower spike. |
Plant at edge of bed. Use in rock garden. Cut flow-er. Thin woodland or shade from shrubs. Naturalize in grass. Coastal conditions |
Grows in open, calcareous, stony and rocky places, hill slopes. Requires winter mulch to protect it from the worst of the weather. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
White with Red stripes
|
September, October, Umbel |
6-12 x 12 (15-30 x 30) Sand, Chalk |
Green cylindrical and hollow leaves |
These unusual autumn flowering species are ideal on a scree or rockery in full sun. They are hardy and also make nice pot specimens in a cold greenhouse. |
Native of the Pelo-ponnese. Plant at soil level and 4 inches (10 cms) apart. All Alliums have the distinctive onion smell, both in the foliage and bulb. This smell can be used to reduce aphid infestations on flowers by planting 1 each side of the infected plant. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Babiana stricta - tender |
Pale Cream through Purple, Mauve and Blue and Crimson
|
March, April, May 5 petal, funnel-shaped flowers in a spike with slight fragrance |
6-18 x 4 |
Sword-shaped 5 inches (12.5 cm) long, 0.5 inches (1.125 cms) wide, green
|
Plant against South-facing House Wall in Southern England where temperatures do not go below -5 degrees Centigrade. Mulch with 3 inches (7.5 cms) of organic compost to conserve moisture in the summer. |
Set 6 inches (15 cms) deep in average and sandy soils, a little shallower in heavy clay - put 2 inches (5 cms) of sand surrounding bulb to prevent rotting - soils, 6 inches (15 cms) apart. Leave undisturbed for years. Remove mulch during autumn and winter. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dark Green to Dark Brown Spathe
|
September, October, November Up to 6 inches (15 cm) long spathe but not a flower |
4-8 x 12 Scree, Sand or Chalky soil with 1 inch (2.5 cms) of sand worked into the top 2 inches (5 cms). |
The 5-10 light green leaves are 1 inch wide and 2-4 inches long.
|
Can be planted beside a path in a rock garden where it is is a rocky, sandy location in full sun in Southern England. |
Biarum is a group of unusual looking bulbs, grown for their weird and wonderful spathes that are produced in autumn. Not fully hardy so these are best grown in pots in the garden before spending the winter in a greenhouse. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Light Green with
|
September, October Up to 6 inches (15 cm) long spathe but not a flower |
3-4 x 12 |
5-10 light Green leaves emerge in Sep-Oct
|
Can be planted beside a path in a rock garden where it is is a rocky, sandy location in full sun in Southern England. |
Not fully hardy so these are best grown in pots in the garden before spending the winter in a greenhouse. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biarum tenuifolium |
Pale Green with Purple Flush Spathe
|
July, August, September, October, November |
10 x 12 |
5-10 light Green leaves emerge in Sep-Oct
|
Can be planted beside a path in a rock garden where it is is a rocky, sandy location in full sun in Southern England. |
Native to the central and eastern Mediterranean. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bright Green with
|
September Up to 6 inches (15 cm) long spathe but not a flower |
9 x 12 |
5-10 light Green leaves emerge in Sep-Oct |
Can be planted beside a path in a rock garden where it is is a rocky, sandy location in full sun in Southern England. |
Native to Northern Greece and Italy. Not fully hardy so these are best grown in pots in the garden before spending the winter in a greenhouse. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
"The Erythroniums native to the Western U.S. are considered by many to be the most beautiful of the genus. Often called "Fawn Lilies" because of the dappled coloring to the leaves, they have dainty nodding flowers like small lilies, set off by large shining leaves that are either plain green or marbled with silver and bronze. Most grow in shaded woodland areas that go quite dry in summer, but with excellent drainage, they can tolerate some summer water." from Telos Rare Bulbs in USA. "Culture in Garden - They like a damp, well-drained soil, and a partially drained position. The bulbs must not be kept out of the ground any longer than necessary, as they resent being moved, nor must the best results be expected at their first time of flowering. It follows that they should be left alone as long as they flower well. An anual top-dressing of a mixture of light decayed manure and peat benefits them. They are increased by offsets and by seed, which last should be thinly sown in pans in a cold frame in August, and the seedlings grown on for 2 years before planted out in the the open; or if room can be found, in loose soil in a cold frame where they remain until the bloom, when the best can be marked before they are put in their permanent places." from Black's Gardening Dictionary. Edited by E.T. Ellis, F.R.H.S. Second edition. Published by A. & C. Black Ltd. in 1928. "The largest flower spikes are found where the ground has recently been burnt, so it is possible that a top dressing of potash would have the same effect. If they are to be divided and moved in the same garden this is probably best done when they are beginning to die down after flowering." from Collins Guide to Bulbs by Patrick M. Synge. Reprinted 173. ISBN 0 00 214016-0 "Suitable for cultivation in the garden, greenhouse or house. They succeed in any good well-drained garden soil, but the ideal compost is equal parts loam, peat, leaf mould and sand. The bulbs should be planted in August in a shady position in beds, rock gardens, edges or under trees. Once planted, they need not be disturbed for many years. "Rock Garden Culture for Erythronium citrinum (Yellow flowers); Erythronium Frans Hals (Purple-rose flowers); Erythronium revolutum (Pink flowers); Erythronium Hartwegii (Creamy-white flowers) - Plant in September 1.5 inches (3.75 cms) deep and 4 inches (10 cms) apart, in partial shade, in moist, well-drained sandy loam and ample leaf-mould or peat. Surround the tubers with about an inch (2.5 cms) of silver sand, and do not lift more often than necessary, but mulch annually with well-rotted manure and leaf-mould. Propagate by means of seed in a frame in August. Thin out but do not plant the seedlings out until the third September after sowing. The plants are also increased by offsets." from Rock Gardens how to plan and plant them with sections on the Wall, Paved, Marsh and Water Gardens by A. Edwards in charge of the rock garden, kew. Published by Ward, Lock & Co. in 1929. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Erythronium |
White,
Each flower stem will have 1-10 downward pointing flowers, with reflexed petals. |
April, May, June Clump. |
6 x 5 Humus-rich Sand. Bulbs must be kept slightly damp during storage and before planting. |
The broad, often mottled, mid-Green marbled purplish- Erythroniums fit in naturally with Trilliums, Galanthus, Hepatica, Helleborus, Hosta, Pulmonaria, Cyclamen coum and Cyclamen hederifolium. |
Grow under deciduous trees/shrubs, in a rock garden, or naturalize in thin grass. Ideally they like a soil which will dry out in Summer although many will do very well in a normal shady bed or border. Must receive adequate moisture during early spring when the foliage is making growth. Appreciates additional dressings of fallen leaves when the plant is in woodland gardens. |
Erythroniums do best when planted under trees and shrubs - to provide partial shade during the hottest part of the day, in as near to a woodland setting as possible. Plant bulbs 5 inches (12.5 cms) deep in good, rich soil; in the autumn in soil that does not dry out. If you want to plant them in pots use a John Innes compost rather than a peat based compost. They will be fine in this and should only be repotted when it is absolutely necessary. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Erythronium |
Sulphur-Yellow with brown central rings
|
April, May, June Forms a large Clump. |
12 x 4 Chalk, |
Bronze-mottled, glossy, deep green |
Plant in pots, woodland or under shrubs in bed. Use as indoor plant in Green-house or sunny window of cool room inside house. Inside Alpine House, or outside in Alpine Trough, or Window-box. |
Bulbs must be kept slightly damp during storage and before planting. A good variety to start off with. Received an 'Award of Merit' in 1959. Ideal compost is equal parts loam, peat, leaf mould and sand for pots. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Erythronium |
Bright Yellow
|
April, May, June Forms a large clump. |
12 x 4 Chalk, |
Wavy-margined, pale to mid-green. |
Plant in pots, woodland or under shrubs in bed. Use as indoor plant in Green-house or sunny window of cool room inside house. |
Plant inside Alpine House, or outside in Alpine Trough, or Window-box. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dark Brown, Maroon and Black
|
October, November, December 6 petal, star-shaped flowers |
16-20 x 16 ( 40-50 x 40) Well-drained Sand, Scree Suitable for coastal conditions in stony or sandy soil. |
Light green leaves overlap each other being up to 12 inches long, with the uppermost surrounding the flowers.
|
The corms should be planted 3-4 inches (7.5-10 cms) deep and 6-8 inches (15-20 cms) apart in pots in a frost-free greenhouse during the winter and then the pots can be sunk into a south-facing rock garden during the summer in bold clumps. |
It grows in dunes and sandy places in South Africa. Flowers may last only one day, but the plant will continue to produce flowers for several weeks from October to early December. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Freesia "For outdoor culture, any light rich sandy soil will suffice, and the bulbs should be planted 2 inch (5 cms) deep and 2 inches apart in August and September. Do not move plants while growing as plants resent being disturbed. "Pot not more than 5 top-sized corms into a 5 inch (12.5 cm) pot from August and onwards, using John Innes compost or 4 parts sand, 3 parts leaf-mould with 0.5 ounces medium bone-meal mixed in the compost. The pots should then be plunged in a sunny spot in the garden, or frame, and remain there until there is the first possibility of frosts. During this time the corms must develop a good length of leaf. Where there is no garden a peat-filled box set up by a sunny window will do as a plunging ground. In such case it is important to see that the peat is kept sufficiently moist and that the excessive heat through the window does not scorch the potting compost. The window should be kept open in hot weather and at all convenient times. |
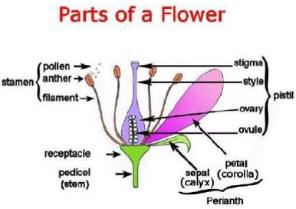
The following details come from Cactus Art:- "A flower is the the complex sexual reproductive structure of Angiosperms, typically consisting of an axis bearing perianth parts, androecium (male) and gynoecium (female). Bisexual flower show four distinctive parts arranged in rings inside each other which are technically modified leaves: Sepal, petal, stamen & pistil. This flower is referred to as complete (with all four parts) and perfect (with "male" stamens and "female" pistil). The ovary ripens into a fruit and the ovules inside develop into seeds. Incomplete flowers are lacking one or more of the four main parts. Imperfect (unisexual) flowers contain a pistil or stamens, but not both. The colourful parts of a flower and its scent attract pollinators and guide them to the nectary, usually at the base of the flower tube.
Androecium (male Parts or stamens) Gynoecium (female Parts or carpels or pistil) It is made up of the stigma, style, and ovary. Each pistil is constructed of one to many rolled leaflike structures. Stigma This is the part of the pistil which receives the pollen grains and on which they germinate. Style This is the long stalk that the stigma sits on top of. Ovary The part of the plant that contains the ovules. Ovule The part of the ovary that becomes the seeds. Petal The colorful, often bright part of the flower (corolla). Sepal The parts that look like little green leaves that cover the outside of a flower bud (calix). (Undifferentiated "Perianth segment" that are not clearly differentiated into sepals and petals, take the names of tepals.)"
The following details come from Nectary Genomics:- "NECTAR. Many flowering plants attract potential pollinators by offering a reward of floral nectar. The primary solutes found in most nectars are varying ratios of sucrose, glucose and fructose, which can range from as little a 8% (w/w) in some species to as high as 80% in others. This abundance of simple sugars has resulted in the general perception that nectar consists of little more than sugar-water; however, numerous studies indicate that it is actually a complex mixture of components. Additional compounds found in a variety of nectars include other sugars, all 20 standard amino acids, phenolics, alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, vitamins, organic acids, oils, free fatty acids, metal ions and proteins. NECTARIES. An organ known as the floral nectary is responsible for producing the complex mixture of compounds found in nectar. Nectaries can occur in different areas of flowers, and often take on diverse forms in different species, even to the point of being used for taxonomic purposes. Nectaries undergo remarkable morphological and metabolic changes during the course of floral development. For example, it is known that pre-secretory nectaries in a number of species accumulate large amounts of starch, which is followed by a rapid degradation of amyloplast granules just prior to anthesis and nectar secretion. These sugars presumably serve as a source of nectar carbohydrate. WHY STUDY NECTAR? Nearly one-third of all worldwide crops are dependent on animals to achieve efficient pollination. In addition, U.S. pollinator-dependent crops have been estimated to have an annual value of up to $15 billion. Many crop species are largely self-incompatible (not self-fertile) and almost entirely on animal pollinators to achieve full fecundity; poor pollinator visitation has been reported to reduce yields of certain species by up to 50%." |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Freesia alba |
White
|
March, 6 petal, funnel-shaped flowers in a cluster. Very strongly scented. |
8-17 x 4 Sand, or potting compost, |
Light Green sword-like leaves
|
Bring pot indoors when nightime temperature drops below 9 degrees Centigrade. Excellent house plants and cut flowers. |
Native to South Africa. Main attraction with these bulbs is the sweet fragrance that fills the room. If outside, mulch in autumn, remove mulch in summer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Freesia andersoniae |
Cream to Purple with yellow.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped flowers in a cluster. Very fragrant. |
8 x 4 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green
|
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Native to southern coastal areas of South Africa. Plant against South-facing House Wall in Southern England |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pale yellow with bright yellow-orange markings.
|
April, May. |
12 x 24 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Erect, spiral dark green fan, 10 inches (25 cms) long.
|
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Native to eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Plant against South-facing House Wall in Southern England |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fragrant Ivory White with mauve reverse and yellow markings.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped flowers in a cluster. |
6-12 x 6 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green
|
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Native to South Africa. In colder areas, lift corms after foliage dies, store overwinter, and replant in the spring. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fragrant Ivory-White
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Introduced in 1957 and recei-ved an 'Award of Merit' in 1962. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fragrant Ivory-White.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dusky Pink on a
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped double-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dark Red on a pale
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped single-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lemon Yellow.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped single-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape |
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Yellow.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped double-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
White.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped double-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Red.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped single-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Creamy-White.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped double-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Buttercup Yellow.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped single-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purple-Red.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped semi-double-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Yellow.
|
April, May. 6 petal, funnel-shaped single-flowered flowers in a cluster. |
10 x 20 Sand, Gravel, or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage held in fan shape
|
Excellent house plants and cut flowers, also in rock garden next to house wall. |
Bring pot indoors during autumn and winter. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Blue Bird' - tender |
Pale Blue and Purple
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Castor' - tender |
Violet Purple
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia flexuosa - tender |
Pinkish Mauve
|
June, July Clump. |
24 x 24 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm |
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Giant' - tender |
Ivory and Purple
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm |
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Hogarth' - tender |
Cream and Purple
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm |
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Holland's Gloire' |
Yellow
|
July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Mabel' - tender |
Pink with Red Blush
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia maculata - tender |
Yellow with Purplish-
|
May, June Clump. |
18 x 12 |
4 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Marquette' - tender |
Yellow and Purple
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm |
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Rose Emperor' |
Pink with
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Titia' - tender |
Magenta
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Venus' - tender |
Dark Red
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm |
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Vulcan' - tender |
Pink and Purple
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ixia 'Yellow Emperor' |
Yellow with
|
June, July Clump. |
16 x 12 |
3-5 erect, narrow, sword-shaped, dark green leaves per corm
|
Grow in greenhouse, cool conserv-atory, patio pot, raised rock garden by south facing wall, window-box. Ground cover |
In very mild areas, plant out in sandy soil with good drainage and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep coarse bark mulch, in March and then lift in late summer when the foliage has died down. Then, corms should be allowed to become dry. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia aloides - |
Green, Crimson and
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
10 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
2 broad-to-lanceolate leaves which are dark green with purple markings
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia aloides |
Yellow
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
10 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
2 broad-to-lanceolate leaves which are dark green with purple markings
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia aloides |
Red, Yellow, Green
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
8-12 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
2 broad-to-lanceolate leaves which are dark green with purple markings
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia aloides |
Bright Orange edged
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12-16 x 12 (30-40 x 30) Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green foliage and flower stems with brown markings
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia aloides |
Greenish-White
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
4-8 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
2 broad-to-lanceolate leaves which are dark green with purple markings
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Very robust |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia bulbifera |
Coral-Red edged with Green or Purple
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
6-15 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
2 broad-to-lanceolate leaves which are dark green with purple spots
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
These are the galleries that will provide the plants to be added to their own Extra Index Pages
The following Extra Index of Bulbs is created in the
Having transferred the Extra Index row entry to the relevant Extra Index row for the same type of plant in a gallery below; then
|
Index of Bulbs from Further details on bulbs from the Infill Galleries:-
---------
|
Bulbs and Corms with
Index of Bulbs from
Website Structure Explanation and
There are other pages on Plants which bloom in each month of the year in this website :-
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia contaminata |
White with Maroon tips and stripes
|
April, May 3 petal, |
6 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Grass-like in appearance and plain Green
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia elegans var. suaveolens |
Blue shading to Rose
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
7-9 x 12 (17.5-22.5 x 30) Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Fransie' |
Pink shading to Yellow with Maroon tips
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green foliage with mid-Green stems spotted Purple
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia glaucina var. pallida |
Cream with a Yellow or Pale Green Hue
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
8 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Dark Green foliage slightly mottled Purple with pale Green flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia juncifolia |
White tinged Red
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
6 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green foliage with mid-Green stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Namakwa' |
Orange fading to Yellow, with Pink tips
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green foliage with Orange flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia namaquensis |
Blue shading to Magenta, White internally
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
6-8 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green foliage
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Spreads rapidly by means of long stoloniferous roots. Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Nova' |
Bluish-Green
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
8 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green foliage with Purple flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia orthopetala |
White
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
10 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green grassy foliage with Purple flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia pustulata |
Cream or Pale Yellow, to Pink or Blue
|
March 3 petal, |
12 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green foliage with Purple flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Robyn' |
Red
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 Sand or potting compost, |
Mid-Green foliage with Purple flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. They can be grown as bed edging in only Southern England, Isle of Wight and Channel Islands within the UK. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Rolina' |
Creamy-Yellow
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 |
Mid-Green with Purple flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Romaud' |
Buttercup-Yellow with Creamy-White tips
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 |
Mid-Green with Purple flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Romelia' |
Light Yellow
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 |
Mid-Green with Purple flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Ronina' |
Yellow
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 |
Mid-Green with Purple flower stems
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Rosabeth' |
Red outer petals, inside is Yellow
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 |
Mid-Green with Purple spots
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia rosea |
Blue through to Pink
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
10 x 12 |
Mid-Green
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia 'Rupert' |
Lilac-Purple
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
12 x 12 |
Mid-Green
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia splendida |
Blue shaded Lilac
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
10 x 12 |
Light Green
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia unifolia |
White with Blue shading
|
May 3 petal, |
10-12 x 12 (20-30 x 30) |
Light Green
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia viridiflora |
Blue-Green to Turquoise
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
8 x 12 |
Mid-Green
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lachenalia zeyheri |
White,
|
March, April, May 3 petal, |
4-8 x 12 |
Mid-Green
|
Edging in frost-free gardens. Houseplant in Patio Pot within a sunny but unheated room. Patio Pot or |
Use either John Innes compost or a mixture of 2 parts sandy loam, 0.5 part leaf-mould and 0.5 part decayed manure, with 1 part coarse sand in pots or hanging baskets. Will not tolerate frost so grow in Greenhouse or as houseplant in a sunny but unheated room. Bed edging in only Southern England. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Leucocoryne 'Andes' |
Mauve with Purple
|
May, June 6 petal, umbel-shaped flower in an umbellate. Sweetly scented. |
10-14 x 4 (25-35 x 10) Well-drained Sand or potting compost, |
Grass-like green foliage varies in length from 6-12 inches. Often they are just maturing or even have died down by going yellow by the time the first flowers are seen. |
A small genus of only 12 species from the winter rainfall regions of South America. These make excellent pot plants in a frost-free greenhouse or unheated room in the house, and |
Plant in the sloping ground next to a South-facing wall in the Channel Islands or in pots in cold frame or greenhouse for the remainder of the UK. The bulbs will not tolerate frost. This plant is resistant to deer! |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Leucocoryne 'Caravelle' |
Mauve with Plum
|
April 6 petal, umbel-shaped flower in an umbellate. Sweetly scented. |
12-16 x 4 (30-40 x 10) Well-drained Sand or potting compost, |
Grass-like green foliage varies in length from 6-12 inches. Often they are just maturing or even have died down by going yellow by the time the first flowers are seen. |
A small genus of only 12 species from the winter rainfall regions of South America. These make excellent pot plants in a frost-free greenhouse or unheated room in the house, and |
Plant in the sloping ground next to a South-facing wall in the Channel Islands or in pots in cold frame or greenhouse for the remainder of the UK. The bulbs will not tolerate frost. This plant is resistant to deer! |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Massonia echinata |
White fading to Pink
|
February Tubular flower |
2 x 10 Well-drained sand or potting mix, |
2 wide green leaves about 5 inches long, which lie flat on the ground.
|
Makes an attractive and unusual late winter flowering pot. Full Sun in a Conservatory in the UK, where temperatures do not fall below 45 degrees Fahrenheit (7 degess Centigrade) in pot or hanging basket |
In well-drained soil (sand) in rock garden within Channel Islands where temperature exceeds 7C, otherwise grow in mixture of 2 parts topsoil, 3 parts peat moss and 7 parts sharp builder's sand in wide pots. Place shards of broken clay pots in the bottom to ensure good drainage. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mela-sphaerula ramosa Zones 8-10 of Hardiness Zone Map developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) |
Pale Yellow
|
April, May, June Tall dainty Gypsophila-like stems are covered with 6 narrow finely pointed petals in small starry flowers within a spray. |
12 x 3-6 Well-drained sand or potting mix, Part Shade in a Conservatory in the UK, where temperatures do not fall below 45 degrees Fahrenheit. Moist in growth, dry in dormancy |
Long, narrow, light green leaves up to !0 inches (25 cms) in length. |
Suits pot cultivation in UK Conservatory. Lasts very well as cut flower. The bulbs will not tolerate frost. Moisture is necessary at the time of planting in late July-September, but keep barely moist until the foliage is observed. Then, additional amounts of water should be given, but never allow the bulbs to sit in cold, wet soil. Should be a complete resting period in the summer with dry conditions. |
Plant 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep and 3-6 inches (7.5-15 cms) apart in the ground next to a South-facing wall in the Channel Islands or 5 bulbs per 10 inch (25 cms) pot and 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep. Soil - In well-drained frost-free soil (sand) perhaps in Channel Islands, otherwise grow in mixture of 2 parts topsoil, 3 parts peat moss and 7 parts sharp builder's sand in wide pots. Place shards of broken clay pots in the bottom to ensure good drainage. Grows in sheltered damp places among rocks in southern Africa. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Magenta-Pink with
|
September |
8 x 4 |
Light green clover-like foliage, often twisting and closing at night or on very hot days. The foliage is not present during the late autumn and winter, when the plant is dormant. |
An outstanding selection with magenta-pink funnel-shaped flowers with yellow throats held above light green clover-like foliage in early autumn. Frost tender, so one for the greenhouse. |
This is good for hanging baskets. Plant 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep and 3-4 inches (7.5-10 cms) apart. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reddish-Purple with
|
September, October, |
0.5-2 x 4 (1.25-5 x 10) |
Light green clover-like foliage, often twisting and closing at night or on very hot days. The foliage is not present during the late autumn and winter, when the plant is dormant. |
This is good for hanging baskets. Plant 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep and 3-4 inches (7.5-10 cms) apart. |
Oxalis is an enormous family of plants from all over the globe. These in this Gallery are a selection of winter-growing varieties. All are easy to grow and very rewarding with very long flowering times. There are approximately 1919 species. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Yellow
|
May, June, July |
4 x 4 |
Small tufts of light green clover-like leaves appear in spring and then die down for several months, before re-appearing in early autumn at the same time as the bright yellow funnel-shaped flowers. Foliage is absent in the winter. Mat-forming habit. Deep mulch after autumn foliage has died down to prevent the bulb being frozen. |
This is good for hanging baskets. Plant 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep and 3-4 inches (7.5-10 cms) apart. |
Frost hardy, this will withstand temperatures down to -5c. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Telos Rare Bulbs in USA have other Oxalis varieties for sale from |
Pink with a Yellow centre
|
May, June, July |
10 x 10 |
Light green clover-like foliage with a silver gloss, often twisting and closing at night or on very hot days. The foliage is not present during the late autumn and winter, when the plant is dormant. |
This is a variable winter-growing oxalis from South Africa which produces delicate flowers in a range of pinks and apricots which last for ages. Do not feed to keep the leaves contained. This is suitable between paving, massed at the front of a low border or in a wall and rock garden, also suitable for window-boxes. Plant 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep and 3-4 inches (7.5-10 cms) apart. |
Oxalis are wonderful "collector's items" -- you know you have been bitten by the bug when, upon seeing their dazzling jewel-like flowers and different leaf forms, you experience an irrepressible urge to possess more! The South African species are largely winter-growers, brightening the dreary months with their exuberant flowers, then go dormant in summer. They are best appreciated as container plants, and need sun to open their flowers. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
White
|
October, November |
5 x 2 |
Light Green, erect, 0.25 inches wide and 4-5 inches high, foliage |
Polyxena is a small family of very dwarf bulbs suited to pot culture in a frost-free situation. Can start to flower in the autumn soon after potting. Very uncommon and well worth growing. This is suitable for hanging baskets in the summer and in coldframes for the rest of the year. Plant 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep and 2-3 inches (5-7.5 cms) apart. Can be grown outside in the Channel Islands in sandy soil. Moisture is needed in early spring, with little or none needed after the foliage dies back in late autumn. |
Small, white flowers are held between the leaves with flower fragrance much like that of a hyacinth. The native habitat in Cape Province of South Africa is open, sparse grassland near the coast. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Deep Lilac
|
October, November |
2-3 x 12 (5-7.5 x 30) |
Light Green, erect, 1 inch wide and 4-6 inches in length, foliage |
This bulb has clusters of starry-like deep lilac flowers produced at the base of the strappy green foliage. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sparaxis grandiflora acutiloba - tender
Sparaxis is derived from the Greek "sparasso" ("to tear"), which refers to the lacerated spathes that surround the flowers |
Golden-Yellow
|
April, May |
4-10 x 12 (10-25 x 30) |
Flat, stiff and rather tough dark Green leaves 8 inches long are held in a fan shape at the base of the flowering spike. |
This is suitable for hanging baskets in the summer and in coldframes for the rest of the year where they can be protected from the frost below 25 degrees Fahrenheit. Plants will withstand a few degrees of frost, but not prolonged cold temperatures. Plant 2 inches (5 cms) deep and 3-4 inches (7.5-10 cms) apart. Can be grown outside in the Channel Islands in sandy soil in bold groups of 25 or more in one place. Moisture is needed in early spring, with none needed after the foliage dies back in late autumn, so that the corms ripen. Great cut flowers, as they are long-lasting. |
Sparaxis, native to South Africa, has been in cultivation for over 200 years, due to its ease and free flowering form. As part of the Iris family, brightly coloured flowers are borne above the strappy foliage. Colours range from hot oranges, yellows and pinks to reds and dark purple. Well worth a pot display in fertile gritty loam under frost free conditions. The plants prefer to be on the dry side in the summer as in their native habitats of South Africa, where they receive their rainfall in the winter. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Deep Violet with
|
April, May |
6-12 x 12 (15-30 x 30) |
Flat, stiff and rather tough dark Green leaves 8 inches long are held in a fan shape at the base of the flowering spike. |
This is suitable for hanging baskets in the summer and in coldframes for the rest of the year where they can be protected from the frost below 25 degrees Fahrenheit. Plants will withstand a few degrees of frost, but not prolonged cold temperatures. Plant 2 inches (5 cms) deep and 3-4 inches (7.5-10 cms) apart. Can be grown outside in the Channel Islands in sandy soil in bold groups of 25 or more in one place. Moisture is needed in early spring, with none needed after the foliage dies back in late autumn, so that the corms ripen. Great cut flowers, as they are long-lasting. |
Sparaxis, native to South Africa, has been in cultivation for over 200 years, due to its ease and free flowering form. As part of the Iris family, brightly coloured flowers are borne above the strappy foliage. Colours range from hot oranges, yellows and pinks to reds and dark purple. Well worth a pot display in fertile gritty loam under frost free conditions. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Yellow and Cream with Purple flush
|
April, May, June |
6-12 x 12 (15-30 x 30) |
Flat, stiff and rather tough dark Green leaves 8 inches long are held in a fan shape at the base of the flowering spike. |
This is suitable for hanging baskets in the summer and in coldframes for the rest of the year where they can be protected from the frost below 25 degrees Fahrenheit. Plants will withstand a few degrees of frost, but not prolonged cold temperatures. Plant 2 inches (5 cms) deep and 3-4 inches (7.5-10 cms) apart. Can be grown outside in the Channel Islands in sandy soil in bold groups of 25 or more in one place. Moisture is needed in early spring, with none needed after the foliage dies back in late autumn, so that the corms ripen. Great cut flowers, as they are long-lasting. |
Sparaxis, native to South Africa, has been in cultivation for over 200 years, due to its ease and free flowering form. As part of the Iris family, brightly coloured flowers are borne above the strappy foliage. Colours range from hot oranges, yellows and pinks to reds and dark purple. Well worth a pot display in fertile gritty loam under frost free conditions. |
Functional combinations in the border from the International Flower Bulb Centre in Holland:- "Here is a list of the perennials shown by research to be the best plants to accompany various flower bulbs. The flower bulbs were tested over a period of years in several perennial borders that had been established for at least three years. In combination with hyacinths:
In combination with tulips:
In combination with narcissi:
For narcissi, the choice was difficult to make. The list contains only some of the perennials that are very suitable for combining with narcissi. In other words, narcissi can easily compete with perennials. In combination with specialty bulbs:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Red, Orange, and Yellow to White with Red and Gold or Black throat
|
May, June, July |
12 x 16 |
Flat, stiff and rather tough dark Green leaves 10 inches long and 0.33 inches wide are held in a fan shape at the base of the flowering spike. |
This corm has Six-petalled flowers, which are produced on wiry stems in early to mid-summer in a wide range of colours from red, orange and yellow to white. In addition some have a very striking red and gold or black throat. The foliage is narrow and strap-like, up to 25cm long. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pale Red
|
May, June |
9 x 16 |
The stiff, pointed, sword-shaped leaves are held in a basal fan and are shorter than the flower spike. |
Tritonia is a small genus of corms from South Africa. Bright flowers are arranged along wiry stems, borne above the grassy foliage. These make a lovely cut flower. The varieties listed in this Gallery are from winter growing regions and so are best cultivated in pots in a frost free situation. Pale Red flowers are erect and bowl-shaped, 1.5 inches in diameter |
This is suitable for hanging baskets in the summer and in coldframes for the rest of the year where they can be protected from the frost below 25 degrees Fahrenheit. Plants will withstand a few degrees of frost, but not prolonged cold temperatures. Plant 2 inches (5 cms) deep and 4-6 inches (10-15 cms) apart. Can be grown outside in the Channel Islands in sandy soil in bold groups of 25 or more in one place in a rock garden. Moisture is needed in early spring, with none needed after the foliage dies back in late summer, so that the corms ripen. In the wild of Cape Province in South Africa, they are found growing in grassy areas where there is considerable moisture during the growing season, followed by a drier period. Great cut flowers, as they are long-lasting. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
White
|
May, June |
9 x 16 |
The stiff, pointed, sword-shaped leaves are held in a basal fan and are shorter than the flower spike. |
This corm has "pure white bowl-shaped flowers. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pink
|
May, June |
10 x 16 |
The stiff, pointed, sword-shaped leaves are held in a basal fan and are shorter than the flower spike. |
This corm has very pretty pink flowers. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pale Red
|
May, June |
10 x 16 |
The stiff, pointed, sword-shaped leaves are held in a basal fan and are shorter than the flower spike. |
This corm has pale red flowers. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Orange
|
May, June |
10 x 16 |
The stiff, pointed, sword-shaped leaves are held in a basal fan and are shorter than the flower spike. |
This corm has hot orange flowers. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The flower stalk is mottled with Purple and is about 18-20 inches in height. Pale Rose and flecked at the tip with Green |
December, January,
|
18 x 30 |
About 10 basal leaves are produced, each up to 18 inches long and 4 inches wide, with undulating margins, forming a rosette. Sometimes flecked with pale green, contrasting well with the shiny deep green. |
This bulb is one for a sunny windowsill or warm greenhouse but well worth growing. A rosette of long fleshy leaves are produced, from the middle of which a single tall flower spike grows. Up to 50 pink, tubular flowers can be borne, the insides are often spotted yellow. Need a minimum of 5 degrees Centigrade (41degrees Fahrenheit). |
Veltheimia bracteata is a native of western areas of the Cape Province of South Africa. This is suitable as a house pot plant. Make sure the containers are large enough so that they can grow for awhile without being repotted. Plant 1 inch (2.5 cms) deep and 6-10 inches (15-25 cms) apart. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Site design and content copyright ©June 2007. Page structure amended November 2012. DISCLAIMER: Links to external sites are provided as a courtesy to visitors. Ivydene Horticultural Services are not responsible for the content and/or quality of external web sites linked from this site. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Recommended Plants for Wildlife in different situations
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
From the Ivydene Gardens Box to Crowberry Wild Flower Families Gallery: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Bumblebee Pages website is divided into five major areas:
FORCED INDOOR BULBS in Window Box Gardens. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Theme |
Plants |
Comments |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Thyme |
Thymus praecox, wild thyme Thymus pulegioides Thymus leucotrichus Thymus citriodorus |
Thymes make a very fragrant, easy to care for windowbox, and an excellent choice for windy sites. The flower colour will be pinky/purple, and you can eat the leaves if your air is not too polluted. Try to get one variegated thyme to add a little colour when there are no flowers. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Herb |
Sage, mint, chives, thyme, rosemary |
Get the plants from the herb section of the supermarket, so you can eat the leaves. Do not include basil as it need greater fertility than the others. Pot the rosemary up separately if it grows too large. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mints |
Mentha longifolia, horse mint Mentha spicata, spear mint Mentha pulgium, pennyroyal Mentha piperita, peppermint Mentha suaveolens, apple mint |
Mints are fairly fast growers, so you could start this box with seed. They are thugs, though, and will very soon be fighting for space. So you will either have to thin and cut back or else you will end up with one species - the strongest. The very best mint tea I ever had was in Marrakesh. A glass full of fresh mint was placed in front of me, and boiling water was poured into it. Then I was given a cube of sugar to hold between my teeth while I sipped the tea. Plant this box and you can have mint tea for months. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Heather |
Too many to list See Heather Shrub gallery |
For year-round colour try to plant varieties that flower at different times of year. Heather requires acid soils, so fertilise with an ericaceous fertilser, and plant in ericaceous compost. Cut back after flowering and remove the cuttings. It is best to buy plants as heather is slow growing. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Blue |
Ajuga reptans, bugle Endymion non-scriptus, bluebell Myosotis spp., forget-me-not Pentaglottis sempervirens, alkanet |
This will give you flowers from March till July. The bluebells should be bought as bulbs, as seed will take a few years to flower. The others can be started from seed. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Yellow |
Anthyllis vulneraria, kidney vetch Geum urbanum, wood avens Lathryus pratensis, meadow vetchling Linaria vulgaris, toadflax Lotus corniculatus, birdsfoot trefoil Primula vulgaris, primrose Ranunculus acris, meadow buttercup Ranunculus ficaria, lesser celandine |
These will give you flowers from May to October, and if you include the primrose, from February. Try to include a vetch as they can climb or trail so occupy the space that other plants can't. All can be grown from seed. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
White |
Trifolium repens, white clover Bellis perennis, daisy Digitalis purpurea alba, white foxglove Alyssum maritimum Redsea odorata, mignonette |
All can be grown from seed. The clover and daisy will have to be cut back as they will take over. The clover roots add nitrogen to the soil. The mignonette flower doesn't look very special, but the fragrance is wonderful, and the alyssum smells of honey. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pink |
Lychnis flos-cucli, ragged robin Scabiosa columbaria, small scabious Symphytum officinale, comfrey |
The comfrey will try to take over. Its leaves make an excellent fertiliser, and are very good on the compost heap, though windowbox gardeners rarely have one. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fragrant |
Lonicera spp., honeysuckle Alyssum maritimum Redsea odorata, mignonette Lathyrus odoratus, sweet pea |
The sweet pea will need twine or something to climb up, so is suitable if you have sliding windows or window that open inwards. You will be rewarded by a fragrant curtain every time you open your window. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Spring bulbs and late wildflowers |
Galanthus nivalis, snowdrop Narcissus pseudonarcissus, narcissius Crocus purpureus, crocus Cyclamen spp. |
The idea of this box is to maximize your space. The bulbs (cyclamen has a corm) will flower and do their stuff early in the year. After flowering cut the heads off as you don't want them making seed, but leave the leaves as they fatten up the bulbs to store energy for next year. The foliage of the wildflowers will hide the bulb leaves to some extent. Then the wildflowers take over and flower till autumn |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Aster spp., Michaelmas daisy Linaria vulgaris, toadflax Lonicera spp., honeysuckle Succisa pratensis, devil's bit scabious Mentha pulgium, pennyroyal |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bee Garden in Europe or North America |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Plants for moths (including larval food plants and adult nectar sources) from Gardens for Wildlife - Practical advice on how to attract wildlife to your garden by Martin Walters as an Aura Garden Guide. Published in 2007 - ISBN 978 1905765041:- |
Marjoram - Origanum officinale |
"On average, 2 gardeners a year die in the UK as a result of poisonous plants. Those discussed in this blog illustrate a range of concerns that should be foremost in the designer’s mind." from Pages on poisonous plants in this website:- |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Wildlife-friendly Show Gardens
Many of our gardens at Natural Surroundings demonstrate what you can do at home to encourage wildlife in your garden:-
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ivydene Gardens Water Fern to Yew Wild Flower Families Gallery: |
Only Wildflowers detailed in the following Wildflower Colour Pages |
|
|||||||||||||||
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
Jun |
Jul |
Aug |
Sep |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
||||||
1 |
Blue |
||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
Cream |
||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
White A-D |
||||||||||||||||
1 Yellow |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
|||||||||||||||||
1 |
Flowering plants of |
||||||||||||||||
1 |
Flowering plants of |
||||||||||||||||